- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- License
- Licenses found
- Syllo/nvtop
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.markdown
- About
- Как узнать статистику использования GPU в Ubuntu?
- NVTOP — мониторинг загрузки видеокарт AMD/NVIDIA
- Intel GPU TOP — для видеокарт от Intel
- How to Check GPU (Intel/AMD/NVIDIA) Usage in Ubuntu 22.04 | 20.04
- Check Intel GPU usage in Ubuntu:
- Monitor AMD/NVIDIA GPU usage in Ubuntu
- Install nvtop in Ubuntu:
- (Optional) Remove nvtop
- How to measure GPU usage?
- 10 Answers 10
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
GPUs process monitoring for AMD, Intel and NVIDIA
License
Unknown, GPL-3.0 licenses found
Licenses found
Syllo/nvtop
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.markdown
Nvtop stands for Neat Videocard TOP, a (h)top like task monitor for AMD, Intel and NVIDIA GPUs. It can handle multiple GPUs and print information about them in a htop familiar way.
Because a picture is worth a thousand words:
NVTOP Options and Interactive Commands
NVTOP has a builtin setup utility that provides a way to specialize the interface to your needs. Simply press F2 and select the options that are the best for you.
You can save the preferences set in the setup window by pressing F12 . The preferences will be loaded the next time you run nvtop .
NVTOP Manual and Command line Options
NVTOP comes with a manpage!
For quick command line arguments help
NVTOP supports AMD GPUs using the amdgpu driver through the exposed DRM and sysfs interface.
AMD introduced the fdinfo interface in kernel 5.14 (browse kernel source). Hence, you will need a kernel with a version greater or equal to 5.14 to see the processes using AMD GPUs.
Support for recent GPUs are regularly mainlined into the linux kernel, so please use a recent-enough kernel for your GPU.
NVTOP supports Intel GPUs using the i915 linux driver.
Intel introduced the fdinfo interface in kernel 5.19 (browse kernel source). Hence, you will need a kernel with a version greater or equal to 5.19 to see the processes using Intel GPUs.
INTEL SUPPORT STATUS
- Intel is working on exposing more hardware information through an HWMON interface. The patches are still a work in progress: see patch series.
- The fdinfo interface does not expose the memory allocated by the process. The field in the process list is therefore empty.
The NVML library does not support some of the queries for GPUs coming before the Kepler microarchitecture. Anything starting at GeForce 600, GeForce 800M and successor should work fine. For more information about supported GPUs please take a look at the NVML documentation.
NVTOP supports Adreno GPUs using the msm linux driver.
msm introduced the fdinfo interface in kernel 6.0 (browse kernel source). Hence, you will need a kernel with a version greater or equal to 6.0 to see the processes using Adreno GPUs.
Several libraries are required in order for NVTOP to display GPU information:
- The ncurses library driving the user interface.
- This makes the screen look beautiful.
- This queries the GPU for information.
Distribution Specific Installation Process
If your distribution provides the snap utility, follow the snap installation process to obtain an up-to-date version of nvtop.
A standalone application is available as AppImage.
Ubuntu Impish (21.10), Debian buster (stable) and more recent
A PPA supporting Ubuntu 20.04, 22.04 and newer is provided by Martin Wimpress that offers an up-to-date version of nvtop , enabled for NVIDIA, AMD and Intel.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:flexiondotorg/nvtop sudo apt install nvtop
sudo apt install libdrm-dev libsystemd-dev # Ubuntu 18.04 sudo apt install libudev-devsudo apt install cmake libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev git
A standalone application is available as AppImage.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and 9
sudo dnf install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-$(rpm -E %).noarch.rpm sudo dnf install nvtopCentOS Stream, Rocky Linux, AlmaLinux
sudo dnf install -y epel-release sudo dnf install nvtop
Build process for Fedora / Red Hat / CentOS:
sudo dnf install libdrm-devel systemd-devel
sudo dnf install cmake ncurses-devel git gcc-c++
A standalone application is available as AppImage.
Build process for OpenSUSE:
sudo zypper install libdrm-devel
sudo zypper install cmake ncurses-devel git
sudo layman -a guru && sudo emerge -av nvtopAn AppImage is a standalone application. Just download the AppImage, make it executable and run it!
# Go to the download location ** The path may differ on your system ** cd $HOME/Downloads # Make the AppImage executable chmod u+x nvtop-x86_64.AppImage # Enjoy nvtop ./nvtop-x86_64.AppImage
If you are curious how that works, please visit the AppImage website.
snap install nvtop # Add the capability to kill processes inside nvtop snap connect nvtop:process-control # Add the capability to inspect GPU info (Fan, PCIe, Power, etc) snap connect nvtop:hardware-observe # AMDGPU process list support (read /proc/) snap connect nvtop:system-observe # Temporary workaround to get per-process GPU usage (read /proc//fdinfo) snap connect nvtop:kubernetes-support
Notice: The connect commands allow
git clone https://github.com/Syllo/nvtop.git && cd nvtop sudo docker build --tag nvtop . sudo docker run -it --rm --runtime=nvidia --gpus=all --pid=host nvtop
git clone https://github.com/Syllo/nvtop.git mkdir -p nvtop/build && cd nvtop/build cmake .. -DNVIDIA_SUPPORT=ON -DAMDGPU_SUPPORT=ON -DINTEL_SUPPORT=ON make # Install globally on the system sudo make install # Alternatively, install without privileges at a location of your choosing # make DESTDIR="/your/install/path" install
If you use conda as environment manager and encounter an error while building nvtop, try conda deactivate before invoking cmake .
The build system supports multiple build type (e.g. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfo):
- Release: Binary without debug information
- RelWithDebInfo: Binary with debug information
- Debug: Compile with warning flags and address/undefined sanitizers enabled (for development purposes)
- The plot looks bad:
- Verify that you installed the wide character version of the NCurses library (libncursesw5-dev for Debian / Ubuntu), clean the build directory and restart the build process.
Nvtop is licensed under the GPLV3 license or any later version. You will find a copy of the license inside the COPYING file of the repository or at the gnu website .
About
GPUs process monitoring for AMD, Intel and NVIDIA
Как узнать статистику использования GPU в Ubuntu?
Ubuntu до сих пор не отображает информацию об использовании графического процессора в системном мониторе. Однако график использования GPU можно легко посмотреть, для этого есть соответствующие программы. Сейчас мы их и рассмотрим.
NVTOP — мониторинг загрузки видеокарт AMD/NVIDIA
Аббревиатура NVTOP расшифровывается как Neat Videocard TOP, она поддерживает большинство современных видеочипов от AMD, NVIDIA. Программа NVTOP отображает использование графического процессора, а также видеопамяти как для отдельного процесса, так и в целом. Дополнительно отображается температура, частоты и энергопотребление.
Теоретически есть поддержка даже видеокарт Intel, но она пока находится в зачаточном состоянии (только драйвер i915). Для AMD поддерживаются все GPU с драйвером amdgpu. Видеокарты NVIDIA поддерживаются, начиная с поколения Kepler (GeForce 600, GeForce 800M и выше).
Для установки NVTOP лучше воспользоваться PPA, так как в официальных репозиториях хранится старая версия (в PPA на текущий момент есть версии для Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04, Ubuntu 22.10 и Ubuntu 23.04).
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:flexiondotorg/nvtop
После установки запустите ее командой nvtop.
Intel GPU TOP — для видеокарт от Intel
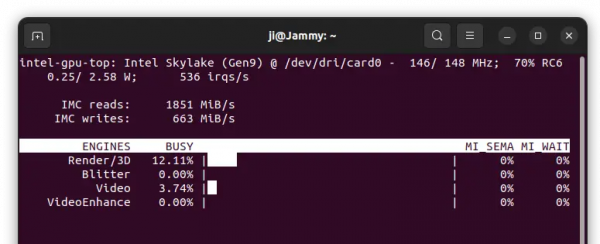
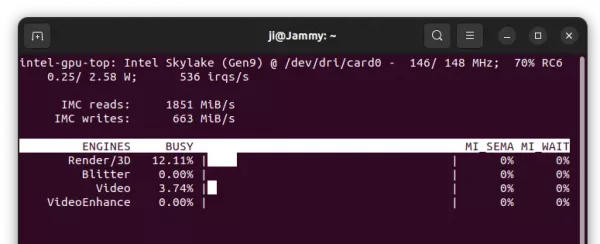
Для графики от Intel также есть аналогичная программа — Intel GPU TOP. Ее интерфейс немного попроще, но основную информацию она отображает: загрузку видеочипа, скорость обмена с видеопамятью, частоты и энергопотребление.
Для установки Intel GPU TOP воспользуйтесь командой:
sudo apt install intel-gpu-tools
How to Check GPU (Intel/AMD/NVIDIA) Usage in Ubuntu 22.04 | 20.04
Unlike Windows, Ubuntu so far does not have real-time GPU usage info displayed in its system monitor application. If you want to check how much your graphic card is in use, then this simple tutorial may help!
Check Intel GPU usage in Ubuntu:
For the integrated Intel graphics card, there’s a command line tool intel_gpu_top can do the job.
1. First, press Ctrl+Alt+T on terminal to open a terminal window. When it opens, run command to install the package:
sudo apt install intel-gpu-tools
Type user password when it asks (no asterisk feedback) and hit Enter.
2. Then, run command to start it:
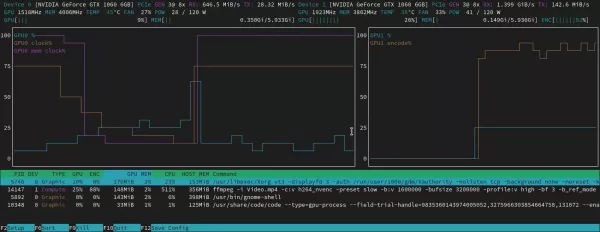
As you can see, it shows real-time IMC read and write speed, power usage, as well as percentage usage of 3D/Render, Blitter, Video, and VideoEnhance.
Monitor AMD/NVIDIA GPU usage in Ubuntu
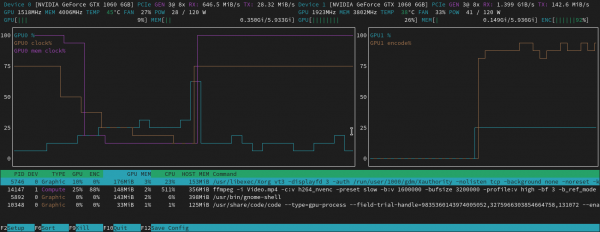
For NVIDIA and AMD graphics card, there’s a htop like task monitor called nvtop (Neat Videocard TOP).
It shows real-time GPU and GPU Memory usage in both total and per process basis, along with temperature, power usage, and graph information.
nvtop, image from https://github.com/Syllo/nvtop
nvtop also supports Intel GPU, however, it does not work in my case with i5-4590 (HD4600), and i3-6006U (HD 520).
Install nvtop in Ubuntu:
The tool is available in Ubuntu system repository, but old. For the latest version, it has an official PPA contains the packages for Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04, Ubuntu 22.10, and next Ubuntu 23.04
1. First, press Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard to open terminal. Then, run command to add the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:flexiondotorg/nvtop
Type user password (no asterisk feedback) when it asks and hit Enter to continue.
2. Then, run command to install the tool:
For Linux Mint, run sudo apt update first to refresh package cache.
Finally, either search for and launch it from ‘Activities’ overview (or start menu), or run nvtop command to start monitoring your GPU.
(Optional) Remove nvtop
To remove the PPA repository, open terminal and run command:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:flexiondotorg/nvtop
And remove nvtop if you want via command:
How to measure GPU usage?
Using the top command in the terminal lists processes, sorted by their CPU usage (and you can change it to sort by another parameter) Is there an equivalent for the GPU? This fellow is asking about RAM used by GPU
Deppending, if you are using a radeon you can use radeontop, for nvidia there’s another tool but I don’t have the name at hand.
For a nvidia gpu, you can use nvidia-smi -l 5 , which will provide an update every 5 seconds. (Change this number to update at a different interval.)
10 Answers 10
- For Nvidia GPUs there is a tool nvidia-smi that can show memory usage, GPU utilization and temperature of GPU.
- For Intel GPU’s you can use the intel-gpu-tools.
- AMD has two options
- fglrx (closed source drivers):
aticonfig won’t work over SSH. Claims it needs an X server running to work (there is one running). However, RadeonTop ( sudo apt-get radeontop ) does work with the fglrx (needs root). Hurrah! Sadly RadeonTop doesn’t provide any temperature readings.
aticonfig WILL work over SSH, but an X server with tcp enabled needs to be running. This can be done by configuring lightdm via xserver-allow-tcp=true . Searching around this site with these keywords should lead to the result.
Not sure why but watch -n 1 nvidia-smi gave me real-time updates. watch nvidia-smi has a 2 sec update delay.
You can use gpustat , which is a simple command-line script (wrapper for nvidia-smi) for querying and monitoring GPU status:
- Install intel-gpu-tools (its likely that they are installed already)
sudo apt-get install intel-gpu-toolsNvidia: to continuously update the output of nvidia-smi , you can use nvidia-smi —loop=1 (refresh interval of 1 second) or nvidia-smi —loop-ms=1000 (refresh interval of 1000 milliseconds).
-l SEC, --loop=SEC Continuously report query data at the specified interval, rather than the default of just once. The application will sleep in-between queries. Note that on Linux ECC error or XID error events will print out during the sleep period if the -x flag was not specified. Pressing Ctrl+C at any time will abort the loop, which will otherwise run indef‐ initely. If no argument is specified for the -l form a default inter‐ val of 5 seconds is used. -lms ms, --loop-ms=ms Same as -l,--loop but in milliseconds.